When it comes to studying language, a lot of fancy terms are thrown around. Phonetics & phonics are two of the most popular. However, very few people have a clear understanding of these two terms. Although these words are spelled similarly, they are NOT the same thing. In this post, we’ll teach you the difference between phonetics vs phonics.
Which Is Correct: Phonics vs Phonetics?
Both phonetics and phonics are nouns with very similar spelling, just like the words denounce or renounce or even pricy vs pricey. The truth is, both words can be correct depending on the context.
- Phonetics: Is the science of describing language sounds. It uses special symbols and terminology to describe the way sounds are made and how they combine to form words.
- Phonics: A system for teaching people how to read. It is based on the idea that there is a relationship between sounds and letters.
Takeaway: Phonetics studies letter & speech sounds. Phonics is the correlation between sounds and letters/symbols in an alphabetic writing system.
When To Use Phonics?
Phonics is the branch of language focused on spoken sounds. It is used to teach people how to read by helping them to understand the relationship between letters and sounds. By learning the sound of each letter, people can begin to read words, even if they don’t know what the words mean. They help to pronounce similar sounding words like annalist and analyst.
Naturally, phonics can also help people to spell words correctly. Understanding the sounds specific groups of letters make for a specific language is critical to developing reading skills and effective literacy instruction.
What Are A List Of Topics Covered In Phonics?
Below are a list of topics that are covered by phonics.
- Grapheme-Phoneme Correspondence. Understanding the relationship between letters (graphemes) and the sounds they represent (phonemes).
- Decoding Skills. Acquiring the ability to convert written words into spoken language through sound-symbol associations.
- Blending: Combining individual sounds to pronounce a word.
- Segmentation. Breaking words into individual sounds for accurate spelling.
- Sight Words. Memorizing and recognizing frequently used words by sight rather than decoding them phonetically.
- Phonemic Awareness. Recognizing and manipulating individual phonemes in spoken words.
- Word Families. Identifying and understanding groups of words that share a common phonetic ending or rime.
- Vowel Patterns. Learning the different ways vowels can represent sounds in words.
- Fluency. Developing the ability to read with speed, accuracy, and expression.
- Orthographic Rules. Understanding spelling conventions and rules governing the arrangement of letters in words.
- Digraphs and Blends. Recognizing combinations of letters that represent distinct sounds, such as “th” or “sh.”
- Morphemes. Grasping the smallest units of meaning in words, including prefixes, suffixes, and root words.
- Word Analysis. Breaking down unfamiliar words to understand their meaning.
- Phonics Rules. Applying rules that govern the pronunciation of sounds in specific linguistic contexts.
- Context Clues. Using surrounding words and sentences to infer the meaning of unfamiliar words.
When To use Phonetics?
Phonetics is the practice of describing language sounds. In order to do this, linguists use special symbols and terms. If you don’t get why proper word choice is important, check out the 5 reasons why grammar is important!
For example, the sound of a ‘b’ in English is different than the sound of a ‘b’ in Spanish. By studying phonetics, we can learn how these sounds are produced and how they differ from one language to another.
Phonetics can come in use when trying to discern the difference between words like flies or flys in your writing!
Is Phonetics A Subset Of Phonics?
No, phonetics is not a subset of phonics. While both fields deal with the sounds of human speech, phonetics is the study of speech sounds in general, including their production, acoustic properties, and auditory perception. Phonics, on the other hand, specifically focuses on the relationship between sounds and written symbols, emphasizing the teaching and decoding of written language.
What Are Phonetic symbols?
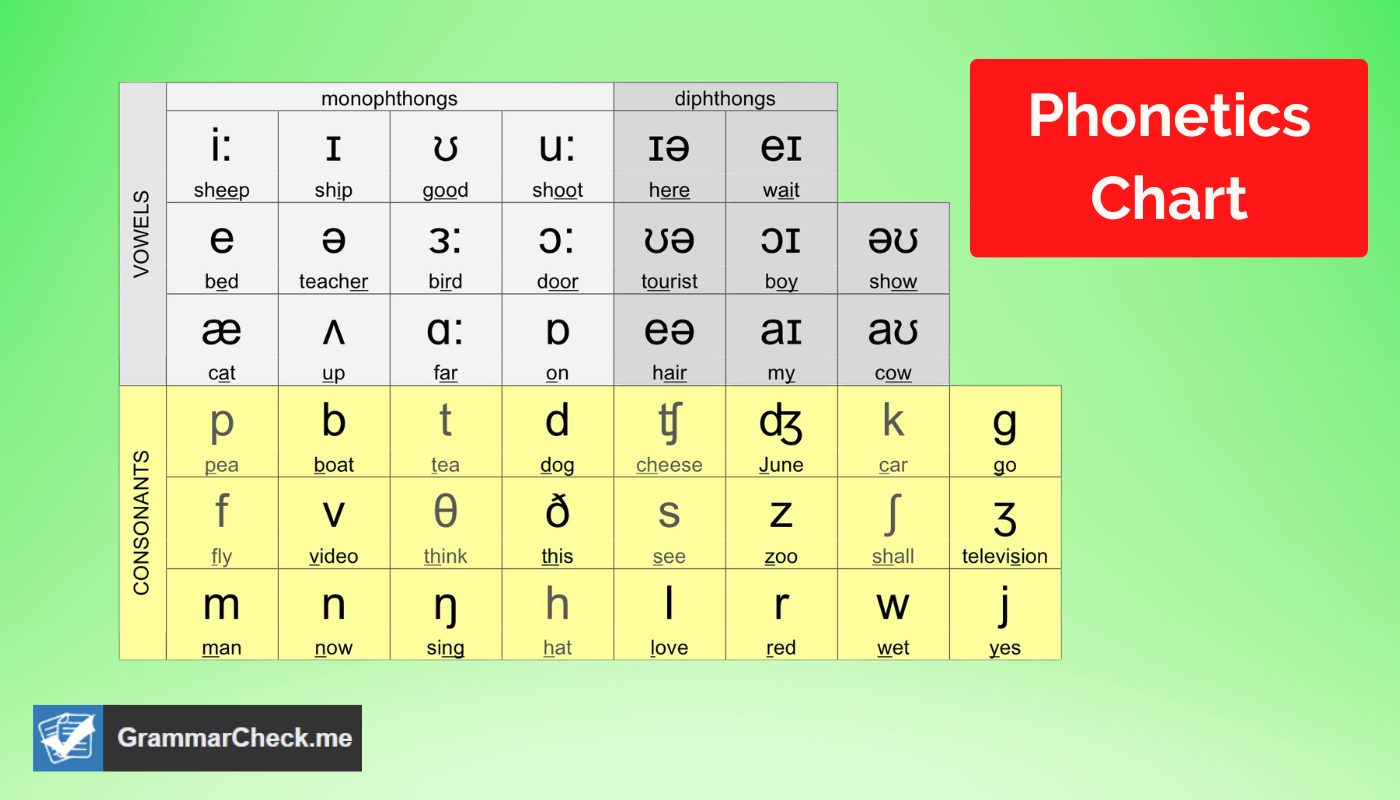
Phonetic symbols represent the different sounds that make up words. They are very important in the construction of basic English spelling rules. They are a useful tool for people who are learning to read, because they can help to break down words into their individual sound units. They can also be helpful for people who are trying to learn a new language, as they can provide a written representation of how words should be pronounced.
International Phonetics Alphabet (IPA)
The International Phonetic Alphabet, or IPA, is an alphabetic system of phonetic symbols that is used primarily in the Latin script.
The IPA is used by linguists to represent the sounds of languages, and it is also used in teaching and learning materials, such as dictionaries and pronunciation guides. It is important for helping people to learn and communicate about language.
Link: International Phonetic Alphabet
Phonological Awareness vs Phonics
Phonological awareness is the ability to recognize and manipulate the spoken parts of sentences and words. Just like with the similar-sounding words exoteric and esoteric!
This includes:
- Ability to hear and produce individual sounds, or phonemes.
- Ability to identify rhyming words, and to break words down into their individual syllables.
- Important building block for reading readiness & teaching an oral language.
FAQs – Phonics vs Phonetics
Phonemic awareness, on the other hand, is the ability to hear, identify, and manipulate the individual sounds that make up words. It is a general awareness that words can be broken down into a series of sounds. Phonics instruction is teaching students to read by linking letters to letter sounds. This can be done with individual or groups of letters in an alphabetic writing system.
Phoneme and phonetics are not the same. Phonetics is the study of human sounds, whereas phoneme is the smallest unit of speech. In other words, phonetics is the scientific study of how speech works, while phonemes are the individual units that make up all spoken words. For example, the word “bat” has three phonemes /b/, /a/, and /t/.
The difference between pronunciation and phonetics is that pronunciation is the act of speaking a word aloud, while phonetics is the study of the spoken sounds of a particular language. In simpler terms, pronunciation is for learning to speak and phonetics is for teaching reading.
Phonemic awareness skills are the ability to focus on and manipulate individual sounds in spoken words. It is an important precursor skill for learning to read, because it enables a person to segment spoken words into their individual phonemes (sounds), which are the building blocks of language.
Not all languages are the same. This is what makes some languages much harder to learn than others. Chinese and Japanese are examples of languages that are not phonetic. In other words, their letters and words are not consistently correlated to how the word sounds.
The English language is phonetic. Generally speaking, around 80-84% of English words are pronounced the way they are spelled.
Yes, German is a phonetic language. A phonetic language is a language in which each sound (or phoneme) is represented by one letter, and one letter represents only one sound. In simpler terms, German words sound exactly how they are spelled.
Basic phonics is the process of matching sounds of spoken English with individual letters or groups of letters. This is an essential skill for people interested in learning to read and spell words. Once you understand the basic phonics concepts, they can apply these skills to reading any word, even unfamiliar words.
There are 5 phonics principles: phonemic awareness, phonics, fluency, vocabulary, and comprehension. Phonemic awareness is the ability to hear and identify the individual sounds in spoken words. Phonics is the ability to use knowledge of letter-sound correspondences to read new words. Fluency is the ability to read quickly and accurately. Vocabulary is the knowledge of words and their meanings. Comprehension is understanding what has been read.
There are 3 types of phonetics: production, transmission, and perception. Production phonetics is the study of how speech sounds are made. Transmission phonetics is the study of how speech sounds are transmitted through the air or other media. Perception phonetics is the study of how speech sounds are perceived by listeners.
The Bottom Line
Now you have a firm understanding of phonetics and phonics. Although both these nouns are similar, they have different definitions, just like causal vs casual. If you didn’t already know, written language and sounds are interconnected. Even though all languages are different, there are patterns seen time and time again. Use these tips to improve your language acquisition skills. And if you can’t seem to master these two words, feel free to use our Sentence Checker!
